As the cryptocurrency space continues to evolve, new blockchain networks and protocols are emerging to address some of the scalability and interoperability issues facing the industry. Two such platforms that have gained significant attention in recent times are Arbitrum and Avalanche.
While both platforms aim to offer solutions for faster, cheaper, and more efficient transactions, they differ in their approach and underlying technology.
In this blog post, we will take a closer look at “Arbitrum vs Avalanche“, compare their features and capabilities, and explore their potential use cases in the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
At a Glance 💡:
- Arbitrum uses Optimistic Rollups as a Layer 2 scaling solution, while Avalanche uses its own consensus protocol as a Layer 1 solution.
- Arbitrum is capable of processing up to 40,000 transactions per second, while Avalanche can handle up to 4,500 transactions per second.
- Both platforms are compatible with Ethereum and other Layer 1 chains.
Arbitrum vs Avalanche: Key Differences
| Key Point | Arbitrum | Avalanche |
|---|---|---|
| Launch Date | 2021 | 2020 |
| Consensus Mechanism | Optimistic Rollups (Layer 2) | Avalanche Consensus Protocol (Layer 1) |
| Token | ARB | AVAX |
| Transaction Speed | Up to 40,000 transactions per second | Up to 4,500 transactions per second |
| Transaction Fees | $0.1 – $0.6 | $0.5 – $1 |
| Smart Contract Capability | Solidity, Vyper | Solidity, Vyper, Rust, C++ (EVM and Non-EVM) |
| Interoperability | Can interact with Ethereum and other L1 chains | Can interact with Ethereum and other L1 chains |
| Security | Uses fraud proofs and challenges | Uses Avalanche Consensus Protocol |
| Governance | Decentralized governance via the Arbitrum forum | Decentralized governance via the Avalanche-X |
| Development Community | Growing | Established |
| Ecosystem Support | Limited at the moment | Growing |
| Use Cases | DeFi, NFTs, DApps, and more | DeFi, NFTs, and more |
What is Arbitrum?

Arbitrum is a layer 2 scaling solution for Ethereum, designed to increase transaction throughput and reduce gas fees. It uses a technology called Optimistic Rollups that bundles multiple transactions into a single batch that’s verified off-chain.
This reduces congestion on the Ethereum network, enabling faster and cheaper transactions. Arbitrum also uses fraud proofs to ensure the security of the network, by allowing users to challenge any invalid transactions.
Read More: Arbitrum Crypto: The Blockchain Of Security & Scalability
What is Avalanche?

Avalanche is a standalone blockchain (also, Layer -1) platform that uses a novel consensus mechanism called Avalanche consensus. This allows for high transaction throughput and low latency by enabling nodes to reach consensus quickly and efficiently.
Avalanche also supports interoperability between different blockchains through its X-Chain and C-Chain networks, which allows for the exchange of assets and data across different blockchain networks.
How Arbitrum and Avalanche Increase Ethereum Scalability?
Arbitrum and Avalanche increase Ethereum scalability by introducing Layer 2 and Layer 1 scaling solutions that allow for off-chain transaction processing. This reduces the burden on the Ethereum mainnet.
Arbitrum uses optimistic rollups to batch transactions off-chain and submit them to Ethereum only when necessary. This significantly reduces the amount of data that needs to be processed by Ethereum, increasing transaction throughput.
In Avalanche consensus, nodes in the network vote on the validity of a set of transactions, using a process called sub-sampling. Nodes sample a subset of other nodes in the network, and they vote on the validity of the transactions based on the votes of those nodes.
This process is repeated several times until the network reaches a consensus on the validity of the transactions. By using this consensus mechanism, Avalanche is able to achieve fast transaction finality in less than one second.
Comparison between Arbitrum and Avalanche (AVAX)
Transaction Speed
TPS is a measure of how many transactions a blockchain platform can process per second. Arbitrum is the fastest L2 with 40,000 transactions per second, which is quite fast.
Avalanche, on the other hand, can handle up to 4,500 transactions per second, which is a slightly lower speed than Arbitrum.
Having a high TPS is important because it means the blockchain can support a large number of users and transactions. Both offer high transaction throughput, which is essential for supporting various decentralized applications and use cases, such as DeFi and NFTs.
Smart Contracts Language
Arbitrum uses the Solidity programming language, which is the same language used for Ethereum smart contracts. This allows for seamless integration with existing Ethereum dApps.
Avalanche, on the other hand, supports multiple smart contract languages including Solidity but also offers compatibility with EVM-based languages such as Vyper, and non-EVM languages such as Rust and C++.
DeFi Ecosystem and TVL
According to Defillama, the TVL on Arbitrum is around $1.77 billion, with a majority of it, locked in DEXs like GMX, Uniswap, and SushiSwap.
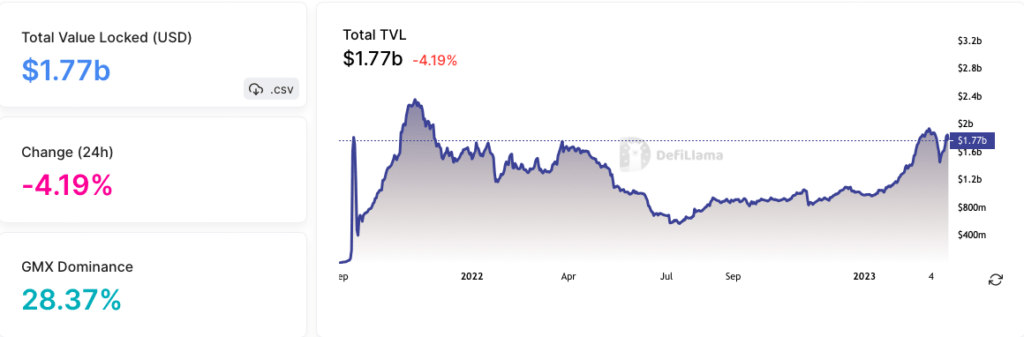
There are several DeFi projects with significant Total Value Locked (TVL). GMX, which operates on two chains, has a TVL of $500.71m. Sushi has a TVL of $129.15m. Camelot, which operates on an Arbitrum chain, has a TVL of $98.14m. Finally, AAVE V3 has a TVL of $91.36m.
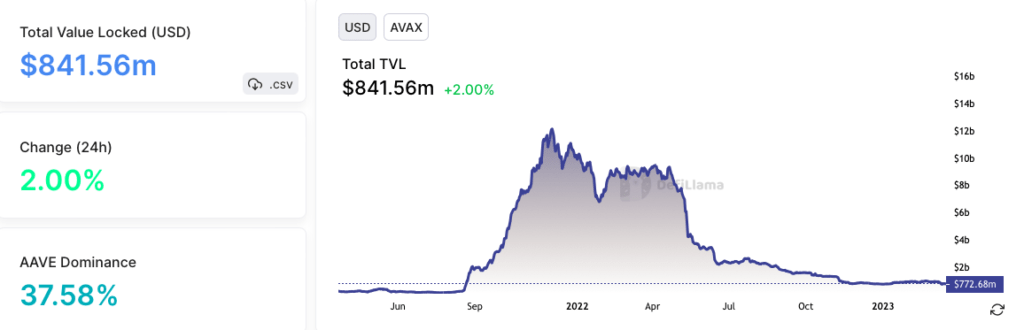
The TVL on Avalanche is around $841 Million, with a significant portion locked in decentralized applications like Aave, Trader Joe, and Benqi. Avalanche has been able to attract a diverse range of DeFi projects due to its high throughput, low fees, and interoperability with other chains.
Related: Avalanche Ecosystem Coins
Token Economics
The native token of the Avalanche network is called AVAX. The maximum token supply of AVAX is capped at 720 million tokens, with around 55% of the tokens already in circulation. AVAX is used as a utility token to pay for transaction fees, staking, and as a governance token.
AVAX holders can participate in on-chain governance decisions, such as proposing and voting on network upgrades, setting network parameters, and more.
Additionally, AVAX is used to secure the network through a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, where validators are required to stake a certain amount of AVAX to participate in block production and validation.
Note: Arbitrum Currently does not have Token, but According to team, ARB Token will be soon in circulation.
Network Security
Avalanche uses a hybrid consensus mechanism called Avalanche Consensus, which combines proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS) protocols. This approach provides a high level of security against 51% attacks and other malicious activities, as well as ensures fast and efficient transaction processing.
Additionally, Avalanche has a network of over 1,000 validator nodes that work together to secure the network and prevent any single entity from controlling a significant portion of the network’s computing power.
Arbitrum, on the other hand, uses a modified version of Ethereum’s proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Optimistic Rollup. It maintains a high level of security through the use of a fraud-proof Mechanism.
Arbitrum Fraud-Proof Mechanism Explained
Arbitrum’s fraud-proof mechanism is designed to prevent invalid transactions from being included in the blockchain. This mechanism allows anyone to submit proof that a transaction is invalid, which can then be used to challenge the inclusion of that transaction in the blockchain.
Validators on the network are then required to review the proof and decide whether to accept or reject it. If the proof is accepted, the transaction is rolled back, and the user who submitted the proof is rewarded with a portion of the fees paid by the invalid transaction.
This approach helps to ensure that only valid transactions are included in the blockchain, which helps to maintain the network’s security and integrity.
Pros and Cons of Arbitrum
Pros:
- Faster and cheaper transactions compared to Ethereum.
- Compatible with Ethereum smart contracts and dApps.
- Uses optimistic rollups which allow for scalability without sacrificing security.
- Can significantly reduce gas fees for users.
Cons:
- Still in its early stages and may have some bugs or issues.
- A limited number of projects are currently deployed on Arbitrum.
- Requires bridging assets from Ethereum to Arbitrum, which can be a complicated process for some users.
- Potential for centralization due to the need for trusted validators.
Pros and Cons of Avalanche
Pros:
- High transaction throughput
- Low transaction fees
- Energy-efficient consensus mechanism
- Built-in support for smart contracts
- Scalability through sharding
- Interoperability with other blockchains
Cons:
- Limited adoption and user base
- Vulnerable to 51% attacks
- Governance structure still evolving
- A limited number of dApps and use cases
How to bridge from Avalanche (AVAX) to Arbitrum?
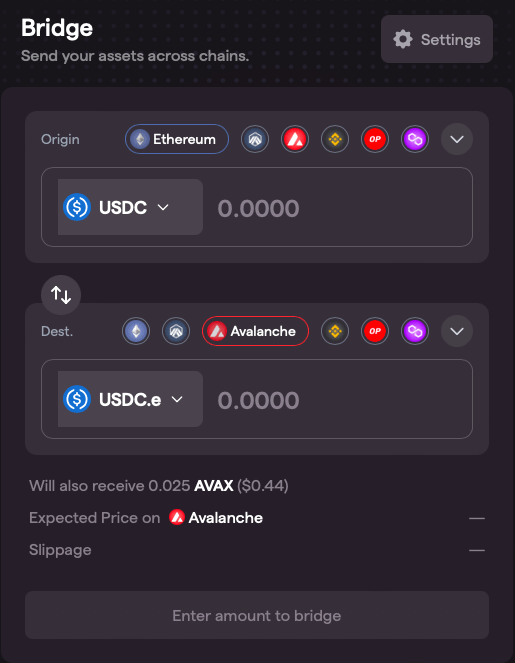
- Access the Synapse Bridge website.
- Choose the AVAX network as the current network, and select Arbitrum as the destination network.
- Indicate the type and amount of the token you want to transfer (e.g., ETH, USDT, USDC, DAI, BUSD).
- Approve the transaction and confirm it using your Metamask wallet.
- Wait for the transfer to complete; the tokens should arrive on Arbitrum in less than two minutes.
Layer-1 vs layer-2: Which is better?
Avalanche is Layer-1, whereas Arbitrum is Layer-2, how they compare:
| Features | Layer-1 | Layer-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Limited by network throughput and block gas limits | Much faster than Layer-1 |
| Transaction Cost | Higher gas fees due to competition for block space | Lower gas fees as transactions are processed off-chain |
| Security | Highest level of security due to decentralized consensus mechanism and censorship-resistance | Relies on trust in the Layer-2 solution’s operators |
| Decentralization | Fully decentralized | Decentralization can be compromised |
| Interoperability | Less | Highly |
| Complexity | Low | High |
| Adoption | Widely adopted | Requires adoption and support from users and developers |
Final Thoughts: Arbitrum vs AVAX
Both Arbitrum and Avalanche are promising Layer-2 and Layer-1 solutions that aim to address the high fees and slow transaction times of the Ethereum network.
Arbitrum offers a simple and secure design with a strong focus on compatibility with Ethereum’s existing ecosystem.
On the other hand, Avalanche provides high scalability, interoperability, and fast finality with its unique consensus mechanism.
Related:



