When it comes to blockchain platforms, the choices can be overwhelming. However, three platforms that have been making waves in the industry are NEAR, Solana, and Fantom.
Each of these platforms has its own unique features and capabilities, but which one is the best fit for your project?
In this blog post, we will take a deep dive into “NEAR vs Solana vs Fantom” and compare their Scalability, Security, Decentralization, and overall performance to help you make an informed decision.
Whether you’re a developer or an entrepreneur, this post is a must-read for anyone considering building on a blockchain platform.
NEAR vs Solana vs Fantom: Market Performace
Here is the comparison between “NEAR vs Solana vs Fantom” based on each blockchain’s market data and Return on Investment after the launch date.
| NEAR | Solana | Fantom | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Market Cap | $1,756,925,483 | $7,818,594,623 | $834,533,839 |
| Circulation Supply | 848,051,611 NEAR | 371,064,855 SOL | 2,771,638,345 FTM |
| Maximum Supply | 1 billion | 371 million | 3.177 billion |
| EVM Support and language | Yes (Aurora) | No (Rust language) | Yes (Javascript) |
| TVL in Defi | $80+ million | $270+ million | $448 million |
| ROI | +71.95% | +9485.61% | +1989.49% |
What is Near Protocol (NEAR)?
The Near Protocol (NEAR) is a decentralized, open-source blockchain protocol designed for fast and scalable smart contract execution.
The main goal of the Near Protocol is to enable the development of decentralized applications (dApps) that are able to handle a high volume of transactions with low latency, low fees, and high security.
One of the key features of the Near Protocol is its use of sharding, a technique that allows the network to be divided into smaller, more manageable pieces called shards.
Each shard processes a portion of the network’s transactions, allowing for increased throughput and faster confirmation times.
The Near Protocol uses a unique sharding mechanism called “Adaptive State Sharding“. This allows the network to adapt to changing conditions and optimize the distribution of transactions across the shards.
Transactions on the network are confirmed in under a second, making it suitable for real-time applications.
The Near Protocol also uses a flexible consensus mechanism called “Nightshade” which allows for a high degree of decentralization and adaptability to changing network conditions.
It also allows for a relatively low barrier to entry for new validators to join the network, helping to ensure a high degree of decentralization.
The Near Protocol is also developer-friendly, with a JavaScript-based smart contract programming language and developer tools like the NEAR Studio.
This is a browser-based development environment for building and deploying smart contracts on the NEAR network.
Additionally, the Near protocol is open-source, meaning that the code can be inspected and improved by anyone, which helps to ensure the security and stability of the network.
What is Solana (SOL)?
Solana (SOL) is a high-performance blockchain platform that utilizes a unique consensus algorithm called “Proof of History” (PoH) to achieve high throughput and low latency.
Some key features of Solana include:
- High scalability: Solana claims to be able to process up to 65,000 transactions per second, which is much higher than other blockchain platforms.
- Low latency: Transactions on Solana are confirmed in under 400 milliseconds.
- Low transaction fees: Because of its high scalability and low latency, Solana can process a large number of transactions at a relatively low cost.
- Decentralized apps (dApps): Solana supports the development of decentralized apps (dApps) and smart contracts, making it a platform for a wide range of decentralized applications.
In addition to its high scalability and low latency, Solana has also seen significant growth in its total value locked (TVL) in the decentralized finance (DeFi) space.
As of January 20, 2023, Solana’s TVL is over $257 million, according to Defillama. This makes it one of the top platforms in the DeFi space in terms of TVL.
Solana also has a strong presence in the non-fungible token (NFT) space, with a number of NFT marketplaces and projects built on the platform.
Some of the popular NFT projects on Solana include SolPunks, Pixelated arts, and Magic Eden, a marketplace for buying and selling NFTs.
What is Fantom (FTM)?
Fantom is a revolutionary blockchain platform that aims to revolutionize the way we use and interact with decentralized networks.
The platform is built on a unique consensus mechanism called “Lachesis”, which allows for near-instant confirmation times and high transaction throughput.
This makes it one of the fastest and most scalable blockchains in the market today.
But speed and scalability are just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to Fantom’s capabilities.
The platform is also incredibly secure, thanks to a combination of proof-of-stake and a unique BFT-DPoS mechanism.
It’s also designed to be interoperable with other blockchains, allowing for seamless communication and cross-chain transactions.
Fantom is also a true definition of decentralization, with no central point of control or failure.
Its open-source codebase allows for community contributions and transparency. And its flexibility allows it to adapt to a wide range of use cases and applications.
NEAR vs Solana vs Fantom: The Ultimate Comparison
Comparing ‘NEAR vs Solana vs FANTOM” based on blockchain technology key points like Transaction speed, block time, gas fees, scalability, and the number of active validators and nodes.
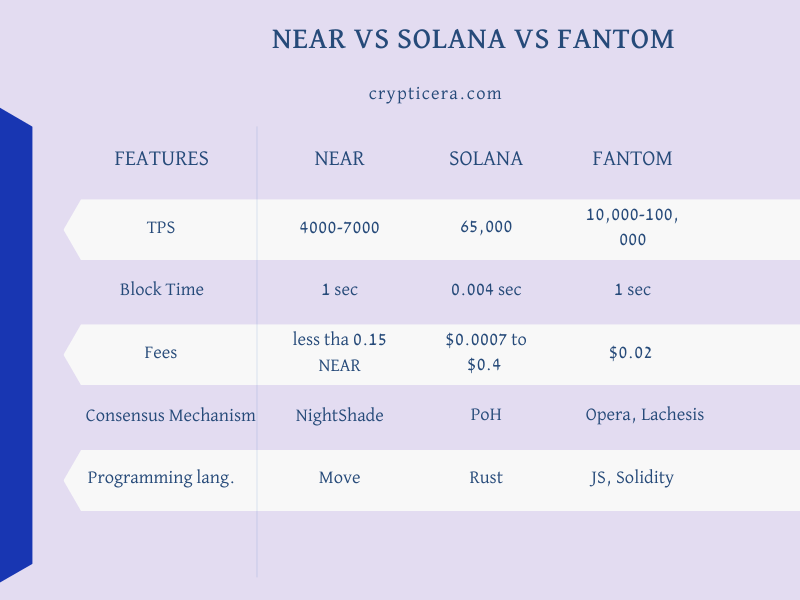
l1 Scalability, TPS, and Consensus mechanism
NEAR: Near Protocol is a sharded, decentralized application platform that uses a unique consensus mechanism called “Nightshade” to achieve high scalability.
The platform can process up to 4,000 transactions per second and has a block time of around 1 second.
Near protocol also uses a sharding mechanism to ensure that the network can handle a large number of transactions without compromising on security or decentralization.
Solana: Solana utilizes a unique consensus mechanism called “Proof of History” (PoH) to achieve high throughput and low latency.
It claims to be able to process up to 65,000 transactions per second, which is much higher than other blockchain platforms.
Solana can confirm transactions in under 400 milliseconds, making it an attractive option for dApps and DeFi applications.
Fantom: Fantom uses the “Opera” consensus algorithm to achieve fast and secure transactions.
The platform claims to be able to process up to 100,000 transactions per second and has a block time of around 1 second.
It also uses a unique form of sharding called “Lachesis” to ensure that the network can handle a large number of transactions without network congestion.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees on Near protocol are based on the computational resources required to execute a smart contract or perform a transfer.
The cost of a transaction is measured in “gas,” and it is less than $1.
As of the time of writing, the transaction fee for each signature on Solana is 5,000 lamports.
Therefore, the total cost for 1,200 transactions would be 6,000,000 lamports or the equivalent of 0.006 SOL. These are very low fees.
Fantom uses a unique fee structure called “Fee Delegation” which allows users to delegate their fees to a validator node. This means that users can perform transactions without paying any fees.
The validator node will then pay the fees on their behalf. This fee structure is designed to make the network more accessible to users and to encourage more participation in the network.
Token Economics and Market Value
The native token of Near Protocol is called “NEAR” and it is used to secure the network and provide incentives for validators and developers. It also serves as a means of exchange for value within the ecosystem.
The current market capitalization of NEAR is around $1.8 billion as of January 20, 2023. The total circulating supply is 848 million NEAR Tokens.
The native token of Solana is called “SOL” and it is used for staking and transaction fees. The staking mechanism allows users to earn rewards for holding and staking their SOL tokens in a validator node.
The current market capitalization of SOL is around $7.8 billion and the Total circulating supply of 371 million SOL Tokens.
The native token of Fantom is called “FTM” and it is used to govern the network.
The current market capitalization of FTM is around $833 million with a circulating supply of 2.77 billion FTM Tokens.
Total Value Locked (TVL)
Total Value Locked (TVL) is a metric that is used to measure the amount of value locked in a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform or protocol.
It is calculated by summing up the value of all assets that are locked in the platform’s smart contracts, such as lending, borrowing, and staking pools.
The TVL is an indicator of the platform’s adoption and growth, and it is used to assess the health and stability of the ecosystem.
A high TVL suggests that there is a large amount of value being locked in the platform, which may indicate high user adoption and confidence in the platform.
- Solana TVL: $257 Million
- Near protocol TVL: $80.6 million
- Fantom (FTM) TVL: $448 million (Source: Defillama)
What is Layer-1 Scalability Solutions?
Layer-1 scalability solutions refer to methods and technologies that aim to improve the scalability of a blockchain network.
This can be achieved by increasing the number of transactions that can be processed per second on the network’s base layer, also known as “Layer-1”.
This is in contrast to Layer-2 scalability solutions, which aim to scale the network by offloading some of the transactions to a separate layer on top of the base layer.
Examples of Layer-1 scalability solutions include sharding, which involves dividing the network into smaller sub-networks called shards. Each of these can process transactions in parallel; and increase the block size, which allows more transactions to be included in each block.
Another approach is using different consensus mechanisms like proof of stake or proof of authority, which allows for faster and more efficient transaction processing.
It’s worth noting that different Layer-1 scalability solutions come with different trade-offs, and each solution may have a different impact on security, decentralization, and other aspects of the network.
NEAR, Solana, and Fantom all are Layer-1 scalability solutions for the main Ethereum blockchain. These networks’ main goal is to solve blockchain Trilemma.
Conclusion
In conclusion, NEAR vs Solana vs Fantom is a well-shouted debate for layer-1 scalability. They are all highly competitive players in the growing world of blockchain technology.
Each platform offers unique features and capabilities that make them well-suited for different use cases.
NEAR is known for its scalability and developer-friendly approach, Solana is praised for its high throughput and low latency, and Fantom is recognized for its fast and secure smart contract execution.
Ultimately, the choice between these platforms will come down to your specific needs and requirements.



