Decentralized finance (DeFi) has emerged as a rapidly growing sector of the cryptocurrency industry.
It offers new and innovative ways to access financial services such as lending and borrowing.
Aave, MakerDAO, and Compound are three popular DeFi projects that offer lending and borrowing services on their respective platforms.
In this blog post, we will compare these three platforms and explore their key features and differences.
We will also examine their lending and borrowing services, staking and governance mechanisms, security protocols, and other key aspects.
Aave vs Compound vs Maker: Differences & Similarities
| Key Points | Aave | MakerDAO | Compound |
|---|---|---|---|
| Launched year | 2017 | 2014 | 2018 |
| Type of platform | Decentralized lending and borrowing platform | Decentralized lending and borrowing platform | Decentralized lending and borrowing platform |
| Native Token | AAVE | MKR | COMP |
| Total Value Locked (TVL) | $22.9 billion USD | $6.3 billion USD | $6.1 billion USD |
| Supported cryptocurrencies | 20+ | 9 | 10+ |
| Interest Rates | Dynamic, based on supply and demand | Dynamic, based on supply and demand | Dynamic, based on supply and demand |
| Collateralized Assets | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Stablecoin Lending | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Flash loans | ✓ | X | ✓ |
| Staking | ✓ | X | ✓ |
| Liquidation process | Automatic | Automatic | Automatic |
| Governance | Token holders vote on platform upgrades and governance issues | MKR token holders vote on platform upgrades and governance issues | COMP token holders vote on platform upgrades and governance issues |
| Security | High | High | High |
| Supported blockchain | Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain | Ethereum | Ethereum |
What is Aave (AAVE)?
Aave (AAVE) is a cryptocurrency and decentralized finance (DeFi) platform that allows users to lend and borrow digital assets.
It is built on the Ethereum blockchain and uses a unique lending pool system to enable users to earn interest on their deposits.
You can also borrow funds from the pool using their deposited assets as collateral.
Aave also offers a range of other DeFi services, including stablecoin issuance and trading on its native exchange.
This makes it a popular platform among cryptocurrency traders and investors looking to earn higher returns through lending and borrowing.
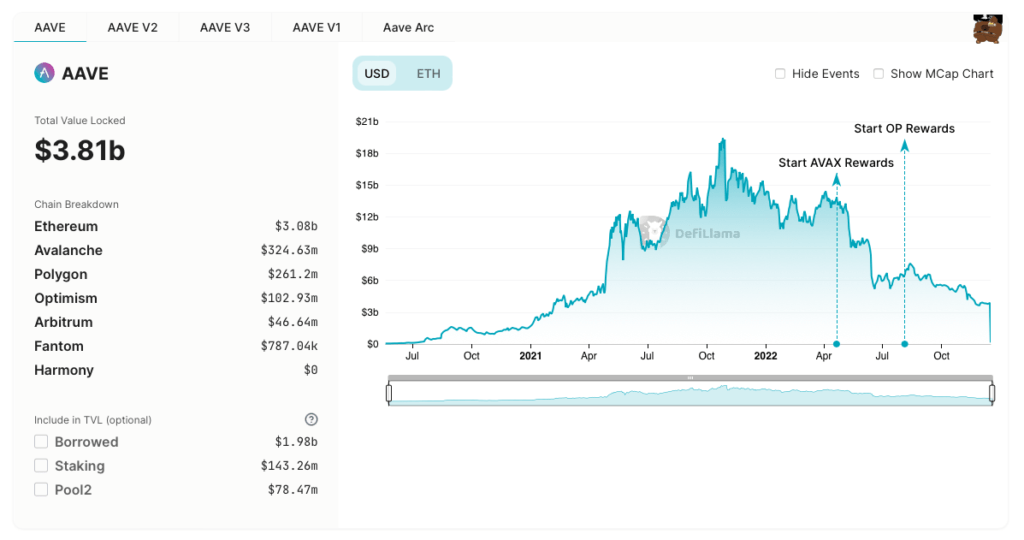
Key Features of Aave
- Support for a variety of cryptocurrencies: Aave allows users to lend and borrow a range of different cryptocurrencies. This list includes popular ones like Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as more niche options like Dai and USDC.
- Multiple lending and borrowing options: These include a traditional lending market, where users can earn interest on their deposited cryptocurrencies. As well as a flash loan feature, which allows users to borrow large amounts of cryptocurrency quickly and without collateral.
- Security: The platform uses a number of security measures to protect users’ funds. This includes secure smart contracts and multi-signature wallet support.
- Integration with other DeFi platforms: Aave is integrated with other DeFi platforms, allowing users to access a range of different financial services within a single ecosystem.
- Governance model: Protocol uses a decentralized governance model. It helps in decentralized decision-making through the use of a token called “LEND.” This allows the Aave community to collectively shape the direction of the platform.
What is Compound Finance (COMP)?
Compound is a protocol built on the Ethereum blockchain that allows users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies.
The protocol is a decentralized finance (DeFi) application built on a blockchain with high security.
In the case of Compound, users can supply cryptocurrencies to the protocol, which are then pooled together and used to provide loans to other users.
The loans are issued in the form of a new cryptocurrency called cToken, which is pegged to the value of the underlying asset.
For example, if you supply Ether (ETH) to the protocol, you will receive cETH, which is pegged to the value of ETH.
One of the key features of Compound is that it uses algorithms to automatically set interest rates for loans based on supply and demand.
This means that the interest rates are determined by the market and can fluctuate depending on how many people are lending and borrowing on the platform.
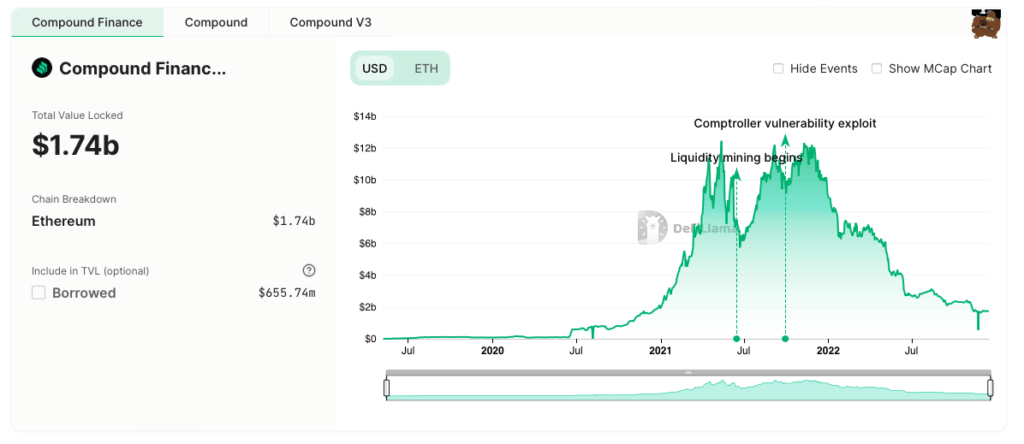
Features of Compound Finance
- Automated interest rates set by algorithms based on supply and demand
- Users can borrow and lend various cryptocurrencies, including Ether, BAT, and ZRX
- A decentralized and trustless platform built on the Ethereum blockchain
- It Can be integrated with other DeFi protocols, such as lending platforms, stablecoin projects, and DEXs
What is MakerDAO (MKR)?
MakerDAO is another decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol that runs on the Ethereum blockchain.
It allows users to borrow funds by collateralizing their assets, creating a stablecoin called Dai. DAI is pegged to the value of the US dollar.
This enables users to take out loans and make payments without needing to go through a traditional financial institution.
MakerDAO is a pioneering project in the DeFi space. It has been instrumental in popularizing the use of stablecoins and smart contracts for financial transactions.
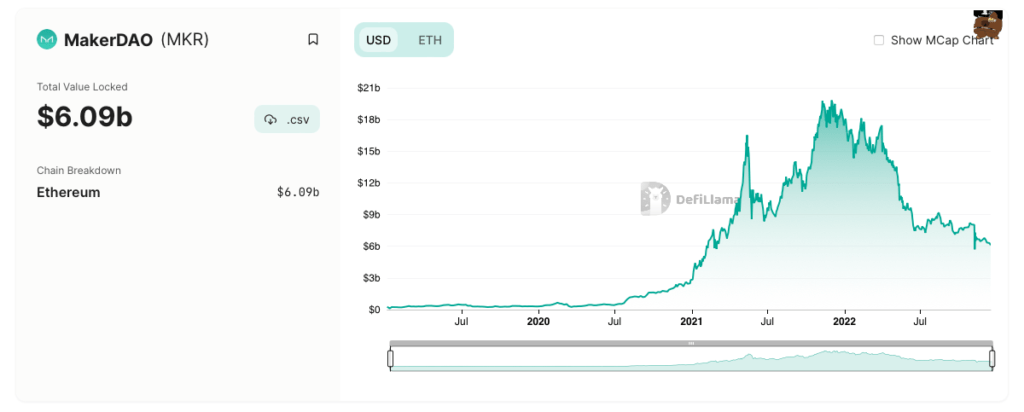
Key Features of Maker
- MakerDAO allows users to collateralize assets, such as ETH, and take out loans in Dai, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar
- Dai is a decentralized, algorithmic stablecoin designed to maintain stability relative to the US dollar
- The protocol is a community-driven, decentralized project with governance carried out by MKR token holders
- MakerDAO uses smart contracts for secure and transparent financial transactions on the Ethereum blockchain
- It Can be easily integrated with other DeFi protocols and dApps to access a range of financial services on Ethereum.
What is Borrowing and Lending in Defi?
Borrowing is obtaining a loan, typically from a bank, with the agreement to pay back the funds and any fees at a later date.
Lending is providing a loan, usually in exchange for interest on the funds.
DeFi facilitates borrowing and lending through smart contracts on blockchain platforms. This allows users to lend and borrow without traditional financial institutions.
Decentralized Finance offers customizable options like variable interest rates and collateral requirements.
Pros and Cons of Defi Lending and borrowing
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Lower fees and interest rates | Relatively new and untested |
| More transparent and accessible | Subject to market volatility |
| Customizable lending and borrowing options | Prone to smart contract bugs |
| The global pool of liquidity | May not offer the same regulatory protection |
| Potential for higher returns on loans | Risk of losses due to platform failures or hacks |
| Ability to lend and borrow without traditional financial institutions | Limited options for dispute resolution and customer support |
| Potential for improved financial inclusion |
What is the difference between MakerDAO and Aave?
MakerDAO and Aave are both decentralized lending and borrowing platforms in the DeFi ecosystem. However, there are some key differences between the two:
- Native Token: MakerDAO’s native token is MKR, while Aave’s native token is AAVE.
- Collateralized Assets: Both platforms allow users to borrow against their crypto assets, but MakerDAO focuses more on stablecoins as collateral, while Aave supports a wider range of cryptocurrencies and assets.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on MakerDAO are determined by MKR token holders, while Aave uses a dynamic interest rate model that is based on supply and demand.
- Liquidation process: MakerDAO uses a “keeper” system where keepers are incentivized to liquidate collateral when it falls below a certain threshold, while Aave’s liquidation process is more automated.
Why is Aave better than Compound?
- Wider Range of Assets: Aave supports a larger number of cryptocurrencies and assets, making it more versatile for users who want to borrow or lend a specific asset.
- Flash Loans: Aave is one of the few DeFi protocols that offer flash loans, which allow users to borrow funds without collateral as long as the funds are returned within the same transaction.
- Gas Efficiency: Aave uses a system called “gas tokenization” which can save users on gas fees when using the platform.
Aave vs Compound vs Maker: Comparison
Interest Rates
Aave uses a unique “flash loan” feature that allows users to borrow funds without collateral.
The interest rates on Aave are determined by the supply and demand for the assets being lent or borrowed, and they can fluctuate based on market conditions.
MakerDAO offers a stablecoin called DAI, which is pegged to the value of the US dollar. Users can borrow DAI by collateralizing other cryptocurrencies.
The interest rate on MakerDAO is fixed at 0.5% per year.
Compound uses an automated interest rate model to set interest rates for borrowers and lenders.
The interest rates on Compound can be calculated by the supply and demand for the assets being lent or borrowed.
Total Value Locked (TVL)
The total value of the assets deposited on these platforms is referred to as the total value locked (TVL).
Here is a comparison of the TVL on these three platforms as of December 2022:
- Aave has the largest TVL of the three platforms, with over $20 billion worth of assets deposited on the platform.
- MakerDAO has a TVL of around $6 billion.
- Compound has a TVL of around $5 billion.
Note: The TVL on these platforms can fluctuate based on market conditions and the amount of assets deposited by users.
Loan to Value (LTV)
Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio is a financial metric that represents the ratio of the loan amount to the value of the collateral pledged. In DeFi lending and borrowing, LTV is an important factor that determines how much collateral a borrower needs to provide to obtain a certain amount of loan.
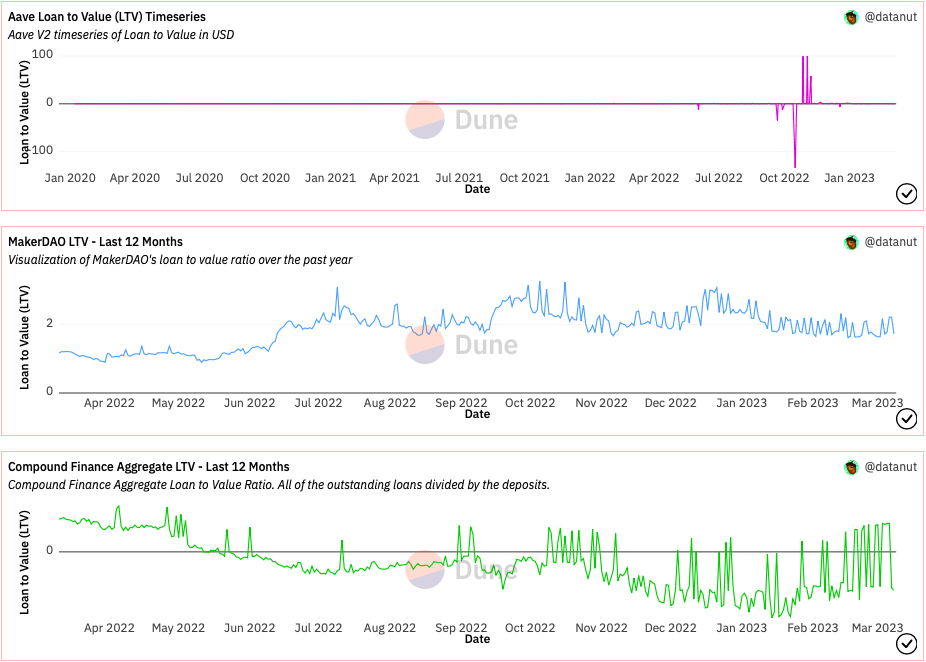
Here’s a comparison of Aave, MakerDAO, and Compound based on their LTV ratios:
| Aave | MakerDAO | Compound | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum LTV | Up to 75% | Up to 66% | Up to 75% |
| Collateralized Assets | Supports a wide range of cryptocurrencies and assets | Supports mainly stablecoins and ETH | Supports a range of cryptocurrencies and assets |
| Liquidation Threshold | 80% | 150% | 85% |
| Liquidation Penalty | 5% | 13% | 8% |
| Dynamic Collateralization | Yes | No | Yes |
From the comparison, we can see that Aave and Compound have a similar maximum LTV ratio of up to 75%, while MakerDAO’s maximum LTV ratio is up to 66%. Aave supports a wider range of collateralized assets compared to MakerDAO, which mainly supports stablecoins and ETH. Compound also supports a range of cryptocurrencies and assets.
In terms of liquidation thresholds and penalties, Aave has a liquidation threshold of 80% and a liquidation penalty of 5%, while MakerDAO has a higher liquidation threshold of 150% and a higher liquidation penalty of 13%. Compound has a liquidation threshold of 85% and a liquidation penalty of 8%.
Finally, Aave and Compound both use dynamic collateralization, which means that the collateral ratio can change depending on the market conditions, while MakerDAO uses a fixed collateralization ratio.
Which DeFi lending service is the best for me?
Aave may be a good choice for users who want to earn interest on both deposited and borrowed assets.
Maker may be a good choice for users who want to avoid the volatility of cryptocurrency by using a stablecoin. But are willing to navigate its more complex collateralization system.
Compound is suitable for users who prioritize high liquidity and competitive interest rates, but are willing to use a smaller selection of supported assets.
Is DeFi lending and borrowing safe?
DeFi lending and borrowing can be relatively safe if users take the necessary precautions and understand the risks involved. Some of the risks associated with DeFi lending and borrowing include:
- Smart Contract Risks: DeFi platforms rely on smart contracts, which can be vulnerable to hacks or bugs that can result in loss of funds.
- Market Risks: The value of cryptocurrencies and assets used as collateral can be volatile, which means that borrowers may find themselves unable to repay their loans if the value of their collateral drops too low.
- Liquidation Risks: If the value of a borrower’s collateral falls below a certain threshold, the collateral may be liquidated to repay the loan, which can result in a loss of funds for the borrower.
To minimize these risks, users should research and choose reputable DeFi platforms, diversify their investments, and use appropriate risk management strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Aave, Maker, and Compound are all popular decentralized finance (DeFi) lending services that offer unique benefits and drawbacks.
Aave allows users to earn interest on both deposited and borrowed assets, offers a wide range of supported cryptocurrencies, and has a user-friendly interface.
Maker offers a stablecoin called Dai that is pegged to the US dollar, allowing users to avoid the volatility of cryptocurrency, but it has a more complex system for collateralizing loans.
Compound offers high liquidity and competitive interest rates, but its supported assets are currently limited to a smaller selection of cryptocurrencies.
FAQs
What are Aave, Maker, and Compound?
Aave, Maker, and Compound are decentralized finance (DeFi) lending platforms that allow users to earn interest on deposited assets and borrow funds using cryptocurrencies as collateral.
What are the main differences between Aave, Maker, and Compound?
The main differences between Aave, Maker, and Compound include the supported assets, interest rates, and collateral requirements.
Aave offers a wide range of supported cryptocurrencies, and competitive interest rates, and allows users to earn interest on both deposited and borrowed assets.
Maker offers a stablecoin called Dai that is pegged to the US dollar but has a more complex system for collateralizing loans.
Compound offers high liquidity and competitive interest rates, but its supported assets are currently limited to a smaller selection of cryptocurrencies.


