If you’re considering investing in a cryptocurrency or building on a blockchain platform, you may be wondering which one is the best option for you.
Cardano and Solana are two popular platforms that have gained a lot of attention in the crypto space, but how do they compare?
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at Cardano and Solana, including their differences, similarities, and which one might be the right choice for you.
Cardano vs Solana (SOL): Similarities and Differences
- Cardano and Solana are two blockchain platforms that aim to provide a secure and scalable platform for decentralized applications (DApps) and smart contracts.
- Cardano uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm called “Ouroboros,” while Solana uses a modified proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm called “Proof of History.”
- Cardano has a focus on financial applications, while Solana aims to support a wide range of decentralized applications across various industries.
What is Cardano (ADA)?
Cardano is a decentralized public blockchain and cryptocurrency project focused on providing a secure and scalable platform for the development and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps).
Cardano was created by blockchain development firm Input Output Hong Kong (IOHK), led by Ethereum co-founder Charles Hoskinson.
It uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm called Ouroboros, which is designed to be more energy-efficient and secure than the proof-of-work (PoW) algorithm used by other cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin.
Cardano’s native cryptocurrency is called ADA and is used to facilitate transactions on the Cardano blockchain.
The Cardano platform is designed to scale quickly and securely, and it is being developed to support a wide range of financial and non-financial applications.
How does Cardano Work?
Cardano’s multi-layer architecture consists of two separate layers: the Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL) and the Cardano Computation Layer (CCL).
CSL is responsible for the bookkeeping and transfer of the cryptocurrency ADA, which uses a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm called Ouroboros to reach a consensus on the state of the blockchain. CSL is designed to be secure, scalable, and efficient, it is the Cardano platform.
CCL is the layer that supports the execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). It is built on top of CSL and designed to be modular and flexible, allowing new features and functionality to be added without breaking existing applications. CCL is still there Under development, not yet fully functional.
The separation of these two layers allows for greater flexibility and scalability, as it enables the platform to be upgraded and enhanced without disrupting ADA’s underlying accounting and transmission.
It also allows for the development of a wide range of applications and uses cases on the Cardano platform, including voting systems supply chain management authentication and financial inclusion
What is Solana (SOL)?

Solana is a decentralized open-source blockchain technology with a focus on scalability and transaction speed. Solana Labs, a software development business situated in San Francisco, California, created it.
Solana has a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus method, which allows users to validate transactions and secure the network by staking or retaining a specific quantity of the platform’s native coin SOL.
Its goal is to create a platform for the development of decentralized apps (dApps) and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, with an emphasis on providing consumers with quick and cheap transactions.
The network promises to be capable of processing up to 65,000 transactions per second, with much cheaper transaction fees than existing blockchain systems.
How does Solana Work?
Solana’s smart contract language is WebAssembly (Wasm). Wasm is a low-level language built for current web browsers and intended for usage as a C, C++, and Rust compilation target.
Solana’s use of Wasm enables developers to build smart contracts in a number of programming languages, rather than only one, as some other blockchain platforms do. This simplifies the development of apps on the Solana platform and allows developers to use their chosen language.
Solana also uses Sealed Ledger technology to validate transactions without disclosing their contents. This contributes to transaction privacy and the prevention of fraud and other harmful behavior on the site.
Furthermore, Solana employs Identity Accounts, which enable users to connect several accounts to a single identity. This is important for isolating transactions or managing different accounts inside a company.
Users can also restore lost or stolen accounts by connecting them to a verified identity.
Key features of the Solana blockchain
- High scalability: Solana can handle thousands of transactions per second
- Fast transaction speeds: Average block time of 400 milliseconds
- Low transaction fees: Utilizes proof-of-stake consensus mechanism
- Decentralized: Not controlled by a single entity or organization
- Open-source: Code is publicly available and modifiable
- DeFi support: Built-in support for decentralized finance applications
- Smart contract support: Allows for self-executing contracts
- Customizable governance: Allows for customization of platform rules and policies
- User-friendly: Easy-to-use interface for building and interacting with DApps.
Cardano vs Solana: The Ultimate Comparison
| Feature | Cardano | Solana |
|---|---|---|
| Launched date | September 29, 2017 | March 31, 2020 |
| Founders | Charles Hoskinson, Jeremy Wood | Anatoly Yakovenko |
| DApps | Yes | Yes |
| Smart contracts | Yes | Yes |
| Market cap | $39.2 billion (as of December 20, 2022) | $13.8 billion (as of December 20, 2022) |
| Transaction speed | Up to 250 transactions per second (tps) | 65,000 tps |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | very High |
| Consensus mechanism | Ouroboros proof-of-stake (PoS) | Proof-of-History (PoH) |
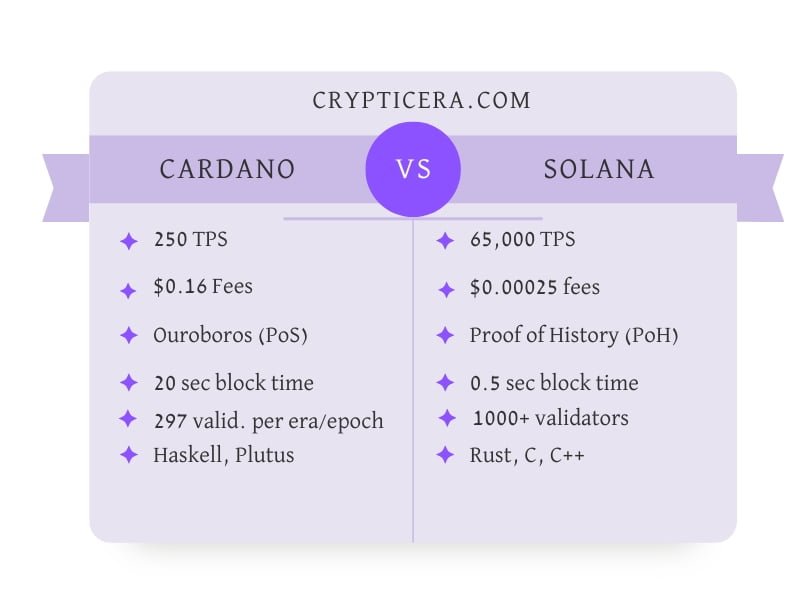
| Programming language | Haskell | Rust |
Smart Contracts and Programming language
The Haskell programming language powers Cardano’s smart contracts, which create decentralized applications such as asset tracking, voting systems, and prediction markets.
The functional programming language’s strong type system and emphasis on correctness ensure the security and reliability of Cardano’s smart contracts.
Solana also uses smart contracts, but with Rust as the programming language. The systems programming language prioritizes safety, concurrency, and speed, with a focus on memory safety.
Solana’s smart contracts also offer high performance and low transaction fees, making them suitable for applications requiring fast and cheap transactions.
Consensus mechanism
Ouroboros is a consensus mechanism used in Cardano that uses proof-of-stake (PoS). It divides the network into epochs and creates a set number of slots at the beginning of each epoch.
A leader is chosen for each slot and it is their responsibility to create and send a block to the network. The more stake a user has in the network, the more likely they are to be selected as a slot leader and contribute to the network.
Solana uses a proof-of-history (PoH) consensus system instead. In PoH, the network maintains a chain of hashes for all past blocks. The current block is created using the hash of the previous block and a “proof” that the block was made at a specific time.
This proof is created by a validator, an external party, who stamps the block with a timestamp based on their own clock.
The validator then broadcasts the block to the network, and other validators verify the block’s integrity and timestamp before adding it to the hash chain.
Transaction Speed
In terms of transaction speed, Cardano is able to process around 250 transactions per second (TPS).
This is faster than many other blockchain platforms, but it is still somewhat slower than some other high-speed platforms such as Solana.
Solana is able to process up to 65,000 TPS, making it one of the fastest blockchain platforms currently available.
This high transaction speed is achieved by using a highly optimized and efficient architecture.
Scalability
Cardano is a blockchain and cryptocurrency that is intended to be safe and capable of handling a high volume of activity. It enables individuals to create smart contracts and employ specialized apps.
Cardano is unique in that it employs a proof-of-stake algorithm rather than a proof-of-work mechanism. This makes transaction processing faster and safer.
Solana is a decentralized blockchain network that is both quick and safe. It employs a proof-of-stake algorithm and a specific manner of conveying information known as a “gossip protocol” to speed up transactions.
Related:
- Polygon Vs Cardano
- Solana vs Cardano vs Polkadot vs Avalanche
- Ethereum vs Cardano vs Polkadot
- Polkadot vs Cardano
- Solana vs Kadena
- Solana vs Aptos
How to Build DApps on Cardano Blockchain?
To build a decentralized application (DApp) on the Cardano blockchain, you will need to use a programming language that is compatible with the Cardano platform.
The most common language for building DApps on Cardano is Haskell, but it is also possible to use languages such as Plutus, which is a purpose-built language for the Cardano platform.
Here are the steps you can follow to build a DApp on Cardano:
- Learn about the Cardano platform and its features to understand what it can do and what tools and languages you can use.
- Pick a programming language that works with Cardano, such as Haskell or Plutus, or use something like Solidity with the right tools.
- Set up a development environment by installing the necessary software and connecting to a Cardano node.
- Create and test your DApp by writing code and possibly making a user interface and smart contracts.
- Finally, publish your DApp on the Cardano network for others to use.
Keep in mind that building a DApp on any blockchain platform requires a strong understanding of distributed systems and blockchain technology, as well as proficiency in programming.
It can be a complex and challenging process, but the rewards of creating a successful DApp can be significant.
How to Build DApps on Solana Blockchain?
To build a decentralized application (DApp) on the Solana blockchain, you will need to perform the following steps:
- Learn about the Solana ecosystem and its features, including the Solana protocol, Rust programming language, and tools and libraries for building DApps.
- Set up a development environment by installing necessary software and tools, including the Solana CLI and Rust, and create a local Solana testnet.
- Design and build your DApp, including the functionality and user interface, and write code to interact with the Solana blockchain.
- Test and fix any issues or bugs in your DApp on the local testnet.
- Deploy your DApp to the Solana mainnet for users to access.
- Monitor and improve your DApp, including fixing any issues or bugs and releasing updates.
ADA vs SOL: Coin Price Analysis
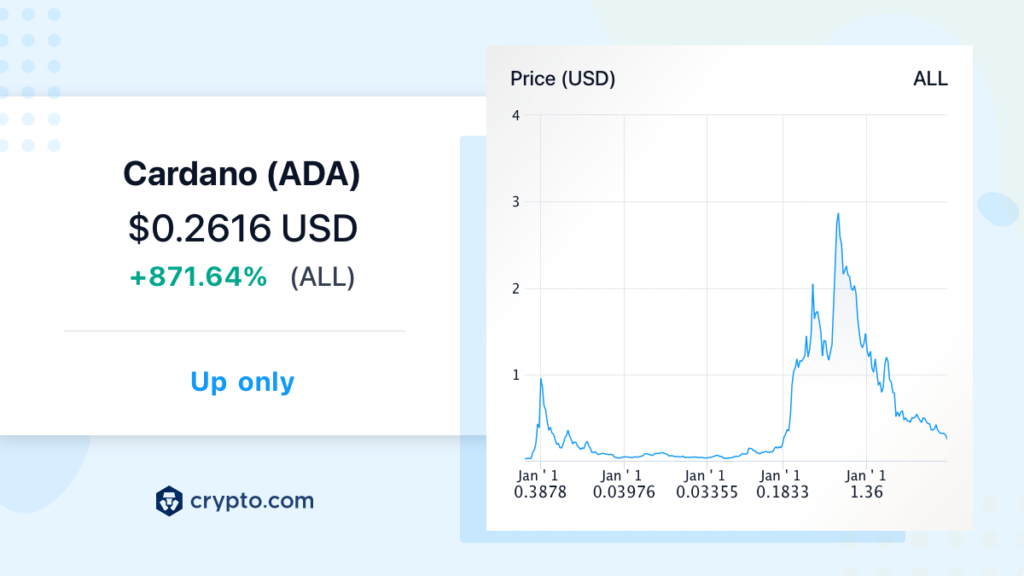
Over the past month, the price of ADA, the cryptocurrency for Cardano, has decreased by 20.67%, lowering its value from $0.32536 to $0.06725. This trend suggests that Cardano may currently be experiencing a dip in value, which could potentially make it a good opportunity to buy ADA.
In the past three months, the price of Cardano has fallen by 42.55%, resulting in a decrease from $0.44927 to $0.19116.
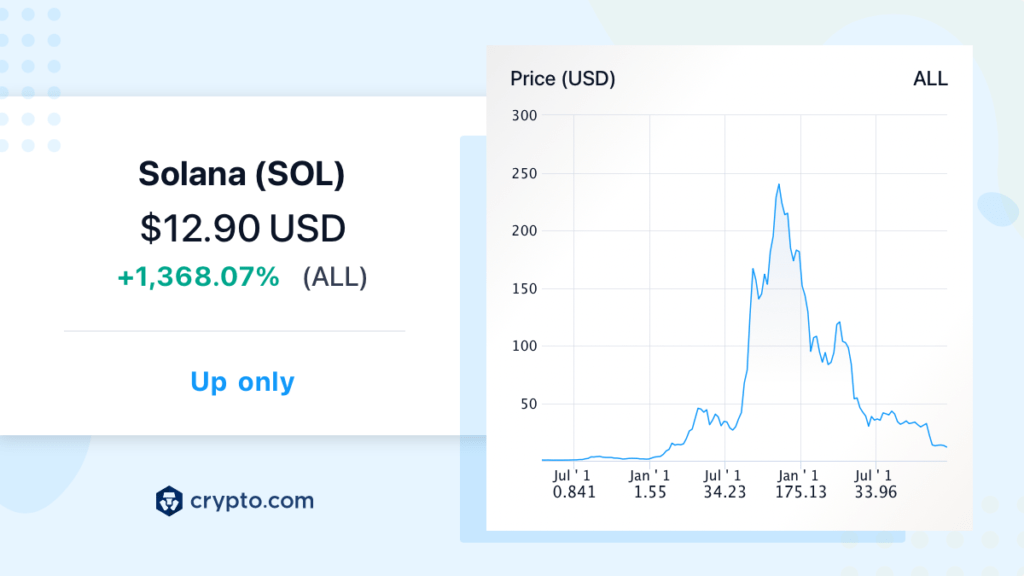
In the past month, the value of SOL has declined by 3.65%, reducing its previous price of $12.82 by $0.46777. This downward trend suggests that Solana is currently experiencing a dip, which may indicate that it is a good time to purchase SOL.
Over the past 90 days, the price of Solana has decreased by 60.99%, resulting in a loss of $19.31 from its previous value of $31.65. Remember, This price dip is all because of FTX Collapse.
Pros and Cons of Using Cardano Blockchain
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Designed for scalability | Limited adoption |
| Strong emphasis on security | Complexity |
| Interoperability with other blockchains | Limited use cases |
| A decentralized governance model allows for a democratic decision-making process and stakeholder input |
Pros and Cons of Using Solana Blockchain
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| High scalability | Limited developer resources |
| Fast transaction speeds | High network congestion issues |
| Low transaction fees | less decentralized governance |
| Energy efficiency | |
| Strong security |
Final Thoughts: Cardano vs Solana
To summarise, Solana and Cardano are both very creative and well-regarded blockchain initiatives. Both technologies prioritize scalability and have proved the capacity to perform a high volume of transactions per second.
Solana employs a novel consensus process known as Proof of History, which aids in the speed and security of transactions. Cardano, on the other hand, employs Ouroboros, a more typical proof-of-stake method.
Both systems have unique capabilities and are continually growing, making it impossible to conclude which is absolutely superior.
Finally, whatever platform to employ will be determined by the user’s individual demands and ambitions.


