Blockchain technology is a rapidly evolving field that has the potential to transform a wide range of industries and applications.
There are many different blockchain projects and platforms that are vying for a place in the market, each with its own unique features, strengths, and weaknesses.
In this blog post, we will compare four of the most popular and promising blockchain projects: Solana vs Cardano vs Polkadot vs Avalanche
We will take a look at their key features, differences, and similarities, and discuss their potential impact on the future of blockchain technology.
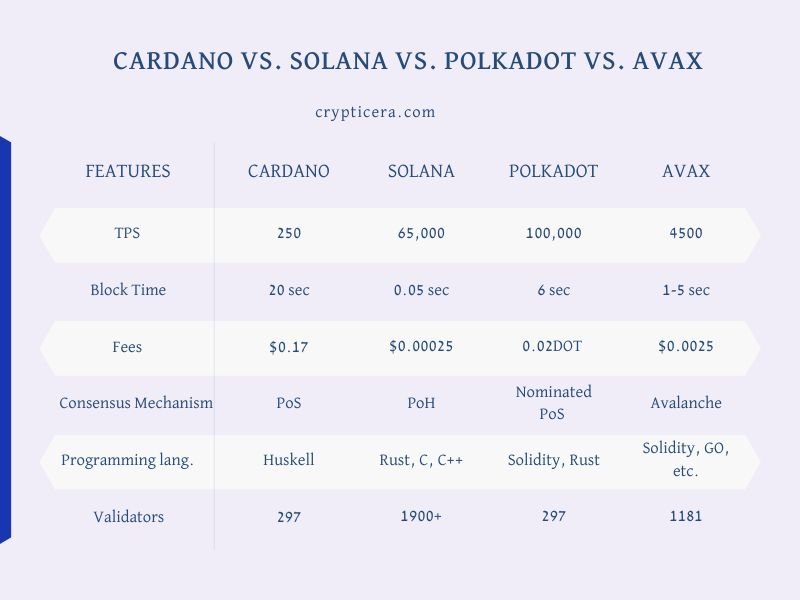
Solana vs Cardano vs Polkadot vs Avalanche: At a Glance
| Solana | Cardano | Polkadot | Avalanche | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Launched date | April 2021 | September 2017 | May 2020 | September 2021 |
| Founders | Anatoly Yakovenko | Charles Hoskinson, Jeremy Wood | Dr. Gavin Wood | Emin Gün Sirer |
| Consensus mechanism | Proof-of-history (PoH) | Proof of Stake | Nominated Proof of Stake | PoS (Snow consensus protocol) |
| Smart contracts | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Scalability | High | High | High | High |
| Programming language | Rust | Haskell | WebAssembly | Solidity, Rust |
| Transaction speed | 65000 tps | 250 tps | 1000 tps practically (100,000 tps theoretically) | 4500 tps |
| DApps | Yes | less number of DApps | Very less | Robust ecosystem |
| Energy consumption | Medium | Low | Low | very Low |
| Algorithm | Proof of History | Ouroboros | Nominated Proof of Stake | CRFG (Correct-by-Construction fork-choice rule) |
| NFTs | Robust NFT Ecosystem | Very less | No | No |
| Market cap | $8.4 billion | $35.4 billion | $45.9 billion | $4.1 billion |
| Token supply | 486 million | 31.11 billion | 997.2 million | 731 million |
What is Solana (SOL)?

Solana is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that provides a fast, secure infrastructure for decentralized applications and other use cases that require high transaction speeds.
It rewards users who hold SOL tokens and participate in the network by using a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism.
Solana’s unique consensus algorithm, Proof of History, enables the platform to achieve finality on transactions within seconds.
This is faster than traditional proof-of-work blockchain systems, which can take minutes or hours.
Solana also ensures the security and scalability of its network through advanced cryptography, network architecture, and a scaling approach called “gauge blocks”.
It can support an increasing number of transactions without sacrificing security or decentralization.
Explore Blockchain: Solana
How does Solana Work?
Solana is a high-speed blockchain network that utilizes a unique consensus algorithm called “Proof of Stake Time” (PoST), or “Proof of history” to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain.
Think of it like a digital conveyor belt, where transactions are the packages and the PoST algorithm is the conveyor belt operator.
The operator ensures that each package is properly sealed and stamped before it’s added to the conveyor belt to be transported to its destination.
The conveyor belt is also incredibly fast, allowing thousands of transactions to be processed every second. This makes Solana a great choice for decentralized applications that require quick and efficient transactions.
Advantages of Solana over other Blockchains
- Solana’s high transaction throughput and low fees make it suitable for fast and efficient transaction processing.
- The Platform supports smart contracts and decentralized apps, enabling the creation of various applications and services.
- Its Proof-of-History protocol efficiently and securely verifies transaction order, eliminating the need for resource-intensive mechanisms like proof-of-work.
- Solana’s “light” client implementation allows users to interact with the network without downloading the entire blockchain, making it more accessible.
- It also hosts popular NFT platforms like Magic Eden, solsea, and Solanart.
Read: Ethereum vs Solana vs Polygon
What is Cardano (ADA)?
Cardano is a decentralized public blockchain and cryptocurrency project. It is a smart contract platform that utilizes a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm called Ouroboros.
ADA blockchain is one of the first blockchains built on scientific philosophy and designed for security, scalability, and interoperability in the development, and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications.
Cardano prioritizes security, scalability, and interoperability.
The platform has a multi-layered architecture that separates the settlement layer (handling Ada transfers) from the computation layer (handling smart contract execution) for flexibility and scalability.
How does Cardano Work?
In PoS systems, validator nodes maintain the blockchain and are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold in the network.
These nodes compete to create new blocks and add them to the blockchain, earning cryptocurrency for their participation.
Ouroboros uses a unique “slot-based” approach for block creation. Each validator node is assigned a specific “slot” in which they can create a new block.
The node assigned to a slot has the exclusive right to create a block for that slot, receiving a reward if they succeed.
This slot-based approach enables Cardano to achieve high transaction throughput and low transaction fees, making it suitable for a variety of applications.
Ouroboros is also designed to be highly secure and resistant to attacks, ensuring the integrity and reliability of the Cardano blockchain.
Advanatages of cardano over other Blockchains
- A two-layer architecture that separates the settlement layer for transactions from the control layer for smart contracts and applications, allowing for greater flexibility and scalability.
- A focus on enabling a wide range of use cases and applications, including decentralized finance (DeFi), supply chain management, and identity verification.
- A commitment to research and development, focusing on advancing the state of the art in blockchain technology and bringing new innovations to the market.
- Cardano has a robust governance model that allows the network to evolve and adapt over time in response to the needs of its users and developers.
Also Read: Cardano vs Solana
What is Polkadot (DOT)?
Polkadot is a decentralized platform that allows different blockchain networks to interoperate.
It aims to create a more decentralized internet where users have more control over their data and online identities. Polkadot enables multiple chains to operate and communicate securely.
Its design features “parachains,” parallel blockchain networks that connect to the Polkadot network and operate alongside each other.
This allows different blockchain projects to share data, transactions, and resources in a decentralized and secure manner.
Polkadot uses a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm called Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) and has a governance model that allows token holders to vote on the direction and development of the network.
How does Polkadot Work?
Polkadot is a blockchain network that uses a unique architecture to enable scalable and interoperable transactions.
It consists of three main components: parachains, parathreads, and the relay chain.
Parachains are independent blockchains connected to Polkadot that can interact with each other. They are designed to handle specific tasks or functions, such as a decentralized exchange or a decentralized finance platform.
Parachains have their own consensus mechanisms and can operate independently of the relay chain.
Parathreads are similar to parachains but more flexible. They can be created and removed as needed for temporary or low-volume transactions that don’t require the same level of security as a parachain.
The relay chain is the backbone of Polkadot and coordinates the activities of the parachains and parathreads.
It provides inter-chain communication infrastructure and ensures that transactions on the network are valid and secure.
Advantages of polkadot Over Other Blockchains
- Support for multiple “parachains” that can run in parallel, allowing for greater scalability and flexibility.
- Use of “relayers” to facilitate interchain communication and interoperability, enabling cross-chain interactions and the creation of multi-chain applications.
- A focus on enabling decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and services, making it an attractive platform for developers working in this space.
- A proof-of-stake consensus mechanism that is designed to be secure and efficient, allowing for high transaction throughput and low transaction fees.
- A growing ecosystem of developers, users, and projects, provides a supportive community and a wide range of resources and tools.
Compare: Polkadot Vs ChainLink
What is Avalanche (AVAX)?

The design of Avalanche is modular and flexible, allowing the creation of multiple parallel blockchain networks, known as subnets, which can operate independently or interact with each other.
This enables different blockchain projects to interoperate and share data, transactions, and other resources in a decentralized and secure manner.
Avalanche employs a unique proof-of-stake consensus algorithm called the Avalanche protocol, designed to be fast, secure, and scalable.
The platform also has a governance model that enables token holders to vote on the direction and development of the network.
How does Avalanche (Work)?
Avalanche, a decentralized finance platform, uses a unique consensus mechanism ” snow consensus protocol”. This allows for fast and secure transactions through a decentralized network of validators.
The validators propose and vote on transactions, and if approved by a majority, the Avalanche platform adds the transaction to the blockchain.
Avalanche’s high transaction processing speed is possible because its mechanism allows for the parallel processing of transactions.
Additionally, Avalanche employs a decentralized network of validators to prevent control by a single entity and ensure the security and integrity of the network.
Advantages of Avalanche Over Other Blockchains
- Faster transaction times: Avalanche can process up to 4,500 transactions per second, compared to traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum which can only handle a few transactions per second.
- Scalability: Avalanche can handle a large number of transactions and users due to its parallel processing capabilities.
- Low latency: Transactions on Avalanche are confirmed in under a second, compared to the minutes or even hours it can take on other blockchains.
- Flexibility: Avalanche allows for the creation of customized subnets, or “Avalanches,” which can be tailored to specific use cases and industries.
- Decentralization: Avalanche uses an algorithm called “Avalanche-X” that allows for a highly decentralized network, with no single point of failure.
- Interoperability: Avalanche can connect and interact with other blockchain networks, enabling the exchange of assets and information between different platforms.
Solana vs Cardano vsAvalanche vs Polkadot: Differences and Similiarites
DApps
Each of these platforms has its own unique features and capabilities, which make them well-suited for different types of DApps.
Some popular DApps on Solana include:
- Serum, a decentralized exchange, and
- Raydium, a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform.
Some popular DApps on Cardano include:
- Plutus, a smart contract development platform, and
- Daedalus is a wallet for storing and managing Ada, the native cryptocurrency of the Cardano network.
Some popular DApps on Avalanche include:
- Trader JOE, a decentralized exchange, and
- Pangolin, a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform.
Some popular DApps on Polkadot include:
- Acala, a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform, and
- Plasm, a smart contract development platform.
Transaction Speed
Solana is a high-speed blockchain platform that is capable of processing up to 65,000 transactions per second.
This makes it one of the fastest blockchain platforms in the market, making it suitable for applications that require high transaction speeds, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and gaming.
Cardano, on the other hand, has a lower transaction per second rate of up to 250 tps.
While this is significantly lower than Solana, Cardano is still considered a fast blockchain platform suitable for applications that require lower transaction speeds.
Avalanche is another blockchain platform that is capable of high transaction speeds, with a rate of up to 4,500 transactions per second.
This makes it suitable for a range of applications, including DeFi and gaming.
Finally, Polkadot is a blockchain platform that has a relatively low transaction per second rate of up to 10-1000 tps.
Energy Consumption
- Solana: Highly energy efficient
- Cardano: Medium energy consumption due to high Market cap which led to network energy congestion
- Avalanche: Low energy consumption compare to Cardano and polkadot
- Polkadot: Lower energy consumption than Cardano but higher than Avalanche
Pros of Solana, Polkadot, Cardano, and Avalanche
Here is a list of key features that are common to Solana, Cardano, Polkadot, and Avalanche:
- Scalability: All are designed to be able to handle a large number of transactions per second without sacrificing security or decentralization.
- Interoperability: The platforms can communicate and interact with other blockchain networks, allowing for the creation of complex and interconnected decentralized applications.
- Open-source: These platforms are open-source, which means that anyone can access and contribute to their underlying codebases.
- Decentralization: All blockchains are decentralized, meaning they are not controlled by any single entity and are run by a distributed network of nodes.
- Security: These platforms are designed to be secure and resistant to tampering or other forms of attack.
SOL vs ADA vs DOT vs AVAX: Coin Price prediction
Cardano: As Cardano (ADA) continues its journey towards making higher highs, our forecast states that in 2023, Cardano will achieve a maximum price of $0.8441 while the average price for the year stands at $0.75366. On the other hand, the minimum price for ADA in 2023 stands at $0.66322.
Polkadot: Polkadot (DOT) price prediction for 2023 states that as the halving approaches, this cryptocurrency will achieve a price of $19.83 in 2025 while the average price of DOT will be $18.26. Meanwhile, the minimum expected price is $16.70.
Solana: As per the algorithmic procedure followed by our technical analysis and prediction, Solana (SOL) will achieve a maximum price of $25.41 as institutional money continues to flow into cryptocurrency. The minimum expected price is $16.94, while the average price will fall around $21.18.
Avalanche: As Avalanche (AVAX) continues to reach new highs, our algorithm expects that in 2023, Avalanche can achieve a maximum price of $37.84 while the average price for the year will stay around $33.78. If a bear market appears, the minimum price AVAX can reach in 2023 is $29.73.
Solana vs Cardano vs Polkadot vs Avalanche: Which is Better “Ethereum Killer”?
| Features | Winner |
|---|---|
| Security | All |
| Scalability | Solana |
| Transaction speed | Solana |
| Privacy protection | Cardano |
| Network congestion resistance | Avalanche |
| Algorithm efficiency | All |
| Energy efficiency | Polkadot |
| Interoperability | Polkadot |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Solana, Polkadot, Avalanche, and Cardano are all popular blockchain platforms that offer unique features and capabilities.
Solana has a high transaction throughput and focuses on decentralized finance applications. Polkadot aims to enable interoperability between different blockchain networks.
Avalanche offers fast transaction finality and support for a wide range of decentralized applications.
Cardano is a proof-of-stake blockchain that prioritizes security and scalability. Each platform has its own strengths and limitations, and it is up to the user to decide which one is the best fit for their specific needs and use cases.



