As the popularity of blockchain technology continues to grow, Ethereum has emerged as one of the leading platforms for creating decentralized applications (DApps) and executing smart contracts.
Both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic are based on blockchain technology and are used to facilitate secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions. However, there are some differences between them that are worth exploring.
In this article, we will explore the differences between “Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic”, including their history, TPS, governance, network architecture, DApps, and future outlook.
Key Takeaways:
- Ethereum Classic is the original blockchain of Ethereum, which remained unchanged after a contentious hard fork in 2016, while Ethereum is the result of the fork and subsequent updates.
- Ethereum operates on a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, while Ethereum Classic continues to use a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism.
- Ethereum has a more centralized governance model, while Ethereum Classic emphasizes a more decentralized and community-driven.
- Ethereum has a more mature and extensive ecosystem of developer tools, libraries, and documentation.
Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic: The Ultimate Comparison
| Key Points | Ethereum | Ethereum Classic |
|---|---|---|
| History | Forked from the original Ethereum blockchain in 2016 | Original Ethereum blockchain |
| Ideology | Blockchain for decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts | Immutability and decentralization principles of blockchain |
| Community | Larger community | Smaller community |
| Market Capitalization | $230 billion | $2.6 billion |
| Algorithm | PoS | PoW |
| Governance | Not Fully Decentralized | Full Decentralized |
| Language | Solidity, and other EVM Compatible | only Solidity |
| Ecosystem | Wider range of dApps, tokens, and DeFi projects built on the platform | A wider range of dApps, tokens, and DeFi projects built on the platform |
| Security | Stronger security measures and bug bounty programs | Relies on security audits and community vigilance |
| Perception | Seen as a more mainstream and popular blockchain platform | Viewed as a more niche and community-driven blockchain platform |
The History of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic
The Birth of Ethereum

Ethereum was first proposed in 2013 by Vitalik Buterin as a blockchain network that would allow developers to build decentralized applications.
The idea was to create a platform that would enable developers to create and execute smart contracts. The main purpose of Ethereum is to create a more secure, decentralized, and programmable blockchain.
Ethereum launched in 2015 after a successful crowdfunding campaign, and quickly gained popularity.
Read More: Guide on Ethereum Blockchain
The DAO Hack
In 2016, a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) was created on the Ethereum network. The DAO was designed to act as a venture capital fund for the Ethereum ecosystem, allowing investors to vote on which projects to fund.
However, a vulnerability in the code of the DAO was discovered, allowing an attacker to drain more than $50 million worth of Ethereum from the fund.
The Ethereum community was divided about how to handle the aftermath of the hack. Some members of the community wanted to reverse the transactions that were made during the hack, while others believed that doing so would go against the decentralized and immutable nature of the blockchain.
Eventually, a hard fork was proposed, which resulted in the creation of two separate blockchains: Ethereum and Ethereum Classic.
Ethereum continued with the new blockchain that reversed the hack, while Ethereum Classic continued with the original blockchain that did not reverse the hack.
The Birth of Ethereum Classic

While the majority of the Ethereum community supported the hard fork, a small group of users and developers believed that the immutability of the blockchain should be maintained. And that the hard fork was a violation of the principles of decentralization.
This group continued to use the original version of the Ethereum blockchain, which became known as Ethereum Classic.
Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic: Technical Differences
Apart from the DAO hack and the subsequent fork, there are some technical differences between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic.
Smart Contracts
Both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic allow developers to create and execute smart contracts.
However, Ethereum has a more advanced smart contract functionality and a larger number of developers working on it than Ethereum Classic.
Ethereum has also introduced new features such as the ERC-20 and ERC-721 token standards, which have become the basis for most of the tokens on the Ethereum blockchain.
Transactions Per Second (TPS)
Ethereum can process around 15-25 transactions per second, while Ethereum Classic can process around 20 – 30 transactions per second.
They both have the same TPS as both works under the same technology. The slight difference is because of high Network congestion on Ethereum due to more transactions happening per second.
However, both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic are working on improving their scalability and increasing their TPS.
Community Support
Ethereum has a larger and more active community than Ethereum Classic. This is because Ethereum has more developers working on it and a larger user base.
Ethereum also has more partnerships and collaborations with other companies and organizations.
Consensus Mechanism
Ethereum Classic uses a proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm, which means that miners solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and earn rewards.
However, Ethereum 2.0 is working on a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, which is expected to be more energy-efficient and secure.
Market Capitalization
Ethereum has a higher market capitalization than Ethereum Classic, which means that it is more widely used and more valuable.
As of now, Ethereum has a market capitalization of around $230 billion, while Ethereum Classic has a market capitalization of around $2.9 billion.
Transaction Fees
One important aspect to consider when comparing Ethereum and Ethereum Classic is the transaction fees.
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic both have high transaction fees, which are paid to miners or stakers to validate transactions on the blockchain.
However, the transaction fees for Ethereum and Ethereum Classic can vary depending on network congestion and demand.
In Ethereum, the typical cost of a transaction fee amounts to 0.002 ETH, while Ethereum Classic levies a mere 0.0001 ETC for the same service.
ETH vs ETC: What Should Developers Consider?
Scalability
Scalability is a critical factor in blockchain platforms as it determines the network’s ability to handle increasing transaction volumes. Ethereum has been facing scalability challenges due to its previous consensus mechanism, Proof of Work (PoW).
As a result, Ethereum decided on transitioning to a new consensus mechanism called Proof of Stake (PoS) through the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. PoS was expected to significantly improve Ethereum’s scalability by reducing energy consumption and increasing transaction throughput.
But, After the upgrade, we have not seen any major difference in its transaction throughput and network congestion.
Additionally, Ethereum has plans to introduce layer 2 scaling solutions, such as Plasma, Sharding, Optimistic Rollups and zk-Rollups. They could further enhance its sustainability by reducing the load on the main blockchain.
On the other hand, Ethereum Classic continues to rely on PoW as its consensus mechanism, similar to the original Ethereum before the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade.
While this ensures security and decentralization, it also limits its scalability potential, as it faces similar challenges with higher transaction fees and slower transaction times during periods of high demand.
DApps
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic are both blockchain platforms that support the development and deployment of decentralized applications (DApps). However, there are notable differences between the two in terms of DApps and their platforms.
Ethereum has established itself as a leading platform for DApps, with a large and vibrant ecosystem of developers, users, and projects.
It boasts a wide range of DApps across various industries, including finance, gaming, decentralized finance (DeFi), Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and more. Some notable examples of DApps on Ethereum include:
- Uniswap – A decentralized exchange (DEX) that enables users to trade cryptocurrencies without relying on a centralized intermediary.
- Aave – It is a leading DeFi protocol that allows users to borrow and lend cryptocurrencies in a decentralized and permissionless manner.
- CryptoKitties – It is an NFT-based game that allows users to collect, breed, and trade digital cats.
- Decentraland – A virtual reality (VR) platform that allows users to create and monetize virtual experiences, including virtual land ownership, gaming, and social interactions.
On the other hand, Ethereum Classic has a smaller ecosystem of DApps compared to Ethereum.
Since Ethereum Classic is a continuation of the original Ethereum blockchain that split after the DAO hack in 2016, it has a smaller community and developer base. However, it still has some notable DApps, including:
- Saturn Network – A DEX built on Ethereum Classic that allows for peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies.
- Emerald Wallet – It is a cryptocurrency wallet for managing Ethereum Classic assets and interacting with DApps on the platform.
- Ethercluster – A blockchain explorer for Ethereum Classic that provides insights into transactions, blocks, and addresses on the network.
Despite its smaller DApp ecosystem, Ethereum Classic aims to provide a decentralized and immutable platform for DApp developers and users who prioritize the principles of blockchain’s original ethos.
Read More: DeFi Guide 101
Total Value Locked [TVL]
Total Value Locked (TVL) is a key metric used to measure the amount of cryptocurrency assets locked within decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols on a blockchain platform. Let’s compare Ethereum and Ethereum Classic based on their TVL.
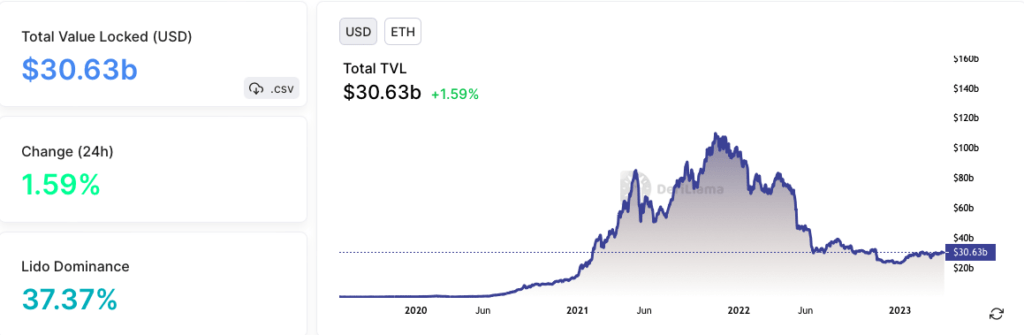
Ethereum’s TVL has consistently been significantly higher than Ethereum Classic’s TVL, indicating a larger share of DeFi activity on Ethereum.
According to data from DeFillama, Ethereum’s TVL has reached $30.63 billion, with various DeFi projects contributing to the growth.
- Lido has the highest TVL at $11.45 billion.
- MakerDAO has a TVL of $7.82 billion.
- AAVE has a TVL of $4.98 billion.
- Curve has a TVL of $4.45 billion.
- Convex Finance has a TVL of $3.78 billion.
- Uniswap has a TVL of $3.61 billion.
Must Read: Best Ethereum Liquid Staking Coins
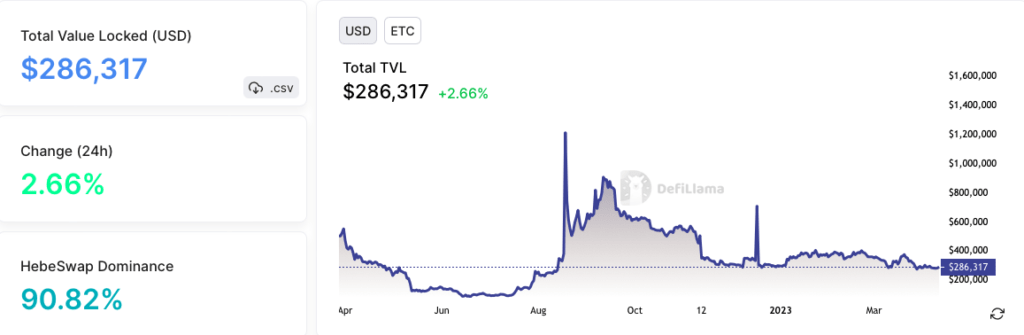
On the other hand, Ethereum Classic’s TVL has been comparatively smaller. While Ethereum Classic has also seen some DeFi projects and protocols being built on its blockchain, its TVL has been notably lower compared to Ethereum. It has a TVL of only $286K, with 90% of its value locked in Hebeswap.
Ethereum vs Ethereum Classic: Which One Should You Choose?
Community and Development
Ethereum has a larger and more active community compared to Ethereum Classic. This means that Ethereum has more developers working on the platform and more resources for development, updates, and improvements.
Ethereum has also been more successful in attracting partnerships with major companies, including Microsoft and JPMorgan.
Innovation and Upgrades
Ethereum has been more aggressive in introducing upgrades and improvements to the platform. The move to proof-of-stake is just one example of Ethereum’s efforts to improve the scalability, security, and sustainability of the platform.
Ethereum’s upgrades have been met with some controversy, but they have also been largely successful in moving the platform forward.
Here are some of the L1 and L2 solutions currently available or in development on the Ethereum network:
- State channels
- Plasma
- Rollups (zk-rollups and optimistic rollups)
- Sharding
- Sidechains
- zkEVM
Use Cases
Ethereum is best known for its support of decentralized applications and smart contracts. Its large developer community has created a wide range of dApps, from gaming and gambling to finance and supply chain management.
Ethereum’s support of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) has also made it a popular platform for digital art and collectibles.
Ethereum Classic, on the other hand, is often seen as a more “pure” version of Ethereum, with a focus on immutability and censorship resistance.
Pros and Cons of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic
Here are some pros and cons of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic:
Ethereum Pros:
- More advanced smart contract functionality
- Larger user base and developer community
- More partnerships and collaborations
Ethereum Cons:
- Lower TPS than Ethereum Classic
- Centralization issues
Ethereum Classic Pros:
- More decentralized and immutable blockchain
- Higher TPS than Ethereum
- Lower risk of hard forks
Ethereum Classic Cons:
- Less advanced smart contract functionality
- Smaller user base and developer community
- High Energy Consumption
PoW vs PoS: Which is better?
| Feature | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus | Miners solve complex mathematical puzzles | Validators are chosen based on their stake (ownership) |
| Resource Usage | High computational power, electricity, and hardware | Very less Resource consumption |
| Security | High security | Low Security |
| Scalability | Less | High |
| Examples | Bitcoin and Ethereum classic | Cardano, Tezos, Ethereum 2.0 |
What are Hard Fork and Soft Fork?
The fork can be initiated by the developers or the community. The developers use the fork to make significant changes to the blockchain network, while the community may initiate the fork to resolve disputes or to improve the network.
There are two types of Fork: Hard Fork and Soft Fork
The hard fork creates a new blockchain network that is incompatible with the old network. Hard forks are usually implemented to make significant changes to the network, such as changing the consensus algorithm, adding new features, or fixing critical hacks.
A soft fork is a backward-compatible change in the blockchain protocol that does not require all nodes to upgrade their software.
The soft fork is achieved by making changes to the existing protocol rules that do not invalidate the old protocol. Soft forks are usually implemented to fix security issues, improve the network’s performance, or add new features to the network.
Learn more: Hard Fork and Soft Fork Detailed Guide
Conclusion
When it comes to the ongoing debate between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic, it’s clear that both chains have their dedicated communities and ideologies.
While Ethereum remains the dominant force in the world of blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi), with its focus on constant innovation and adoption of new technologies. Ethereum Classic has stood its ground as a resilient and immutable chain that upholds the principles of decentralization and immutability to the core.
As we’ve explored in this blog post, Ethereum and Ethereum Classic have taken different paths due to the contentious hard fork that occurred after the infamous DAO hack.
For investors, developers, and enthusiasts alike, the choice between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic ultimately comes down to personal beliefs, risk tolerance, and investment strategy.
Ethereum may offer a broader ecosystem of applications and scalability solutions, while Ethereum Classic may appeal to those who prioritize the principles of immutability and decentralization above all else.


